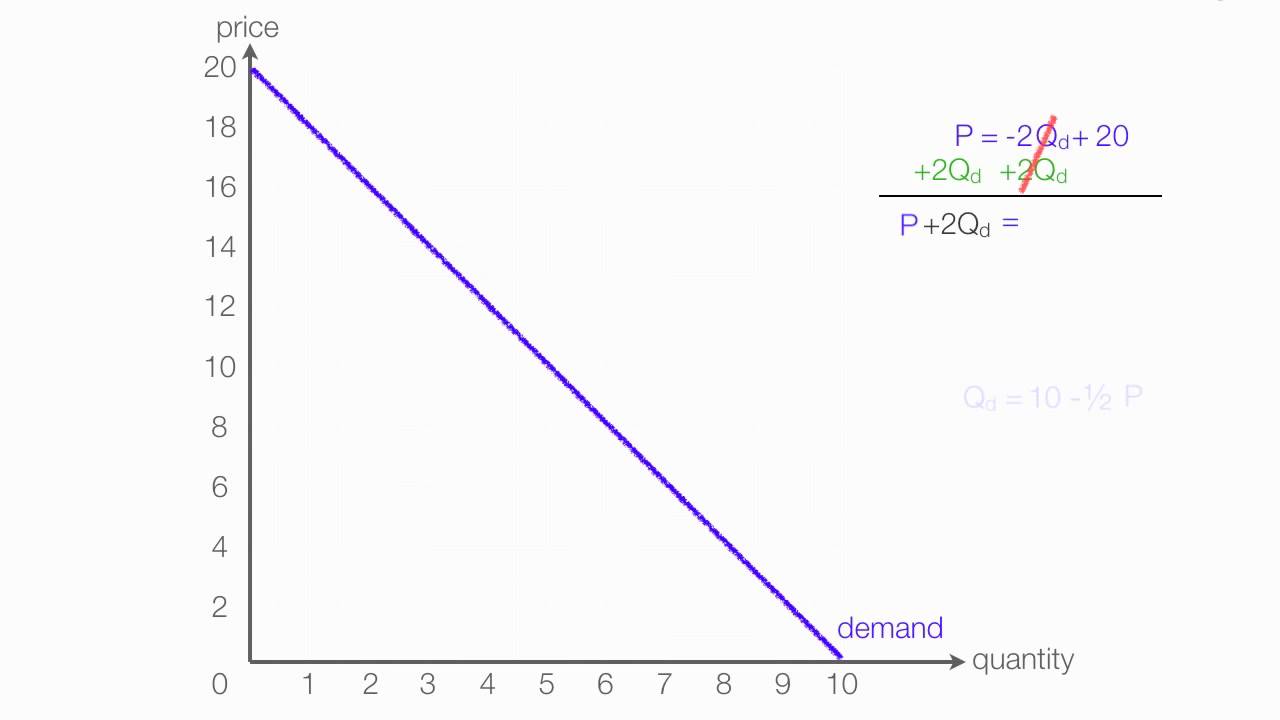
When diving into the realm of economics, one of the crucial concepts to grasp is the inverse demand curve formula. This formula serves as a vital tool for understanding how the price of a good or service influences the quantity demanded by consumers. In essence, it flips the traditional demand curve on its head by expressing price as a function of quantity demanded, rather than the other way around. The significance of this concept cannot be overstated, especially for businesses and policymakers seeking to make informed decisions based on consumer behavior.
As we explore the inverse demand curve formula, it's essential to recognize its practical applications. For instance, businesses can utilize this formula to set optimal pricing strategies that maximize their revenue while considering consumer demand. Additionally, it helps economists and analysts forecast market trends and shifts in consumer preferences, which are vital for strategic planning and resource allocation. By understanding how price changes impact demand, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of supply and demand dynamics.
In this article, we will delve deep into the inverse demand curve formula, breaking down its components and applications in a clear and accessible manner. Whether you're an aspiring economist, a business owner, or simply someone interested in understanding market behavior, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into how this formula operates and its importance in the broader economic landscape.
What is the Inverse Demand Curve Formula?
The inverse demand curve formula is a mathematical representation that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by consumers. It is generally expressed as:
P = a - bQ
In this formula:
- P represents the price of the good.
- a is the price intercept (the price when quantity demanded is zero).
- b is the slope of the demand curve, indicating how much the price decreases as quantity demanded increases.
- Q represents the quantity demanded.
How Does the Inverse Demand Curve Formula Work?
To understand the workings of the inverse demand curve formula, let’s break it down further. The formula essentially expresses how consumers react to changes in price. When the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded typically increases, and vice versa. This relationship is fundamental to the law of demand, which states that, all else being equal, an increase in price results in a decrease in quantity demanded.
Why is the Inverse Demand Curve Important?
The inverse demand curve is crucial for several reasons:
- It allows businesses to predict how changes in pricing will affect sales.
- It helps economists gauge consumer behavior and market dynamics.
- It facilitates optimal resource allocation in production and marketing strategies.
What are the Applications of the Inverse Demand Curve Formula?
The inverse demand curve formula has various applications, including:
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses can use this formula to determine the best pricing strategy to maximize profits.
- Market Analysis: It helps analysts predict how changes in economic factors will impact consumer demand.
- Policy Making: Governments can assess the impact of taxes, subsidies, and regulations on consumer behavior.
How to Calculate the Inverse Demand Curve?
Calculating the inverse demand curve involves rearranging the standard demand equation. For example, if the demand equation is given as:
Q = a - bP
You can rearrange this to derive the inverse demand curve:
P = (a - Q) / b
This transformation allows you to express price as a function of quantity demanded.
Can the Inverse Demand Curve Shift?
Yes, the inverse demand curve can shift due to various factors. Common reasons for shifts include:
- Changes in Consumer Preferences: If consumers suddenly prefer a product more, the demand curve will shift to the right.
- Income Changes: An increase in consumer income can lead to a higher demand for normal goods.
- Substitutes and Complements: The introduction of substitute or complementary goods can also impact demand.
What are the Limitations of the Inverse Demand Curve Formula?
While the inverse demand curve formula is a powerful tool, it does have limitations:
- Assumption of Ceteris Paribus: The formula assumes that all other factors remain constant, which is rarely the case in real markets.
- Linear Representation: The formula represents a linear relationship, which may not accurately reflect the complexities of real-world demand.
Conclusion
The inverse demand curve formula serves as a vital framework for understanding the relationship between price and quantity demanded. By grasping this concept, businesses, economists, and policymakers can make informed decisions to navigate the complexities of market dynamics effectively. Whether it’s optimizing pricing strategies or analyzing market trends, the inverse demand curve remains a fundamental aspect of economic theory.
You Might Also Like
Creative Alternatives: What Can I Substitute For Milk Powder?Understanding The Capacity: How Many Outlets Per 20 Amp Circuit?
Understanding The Weight Conversion: 134lbs In Kg
Finding Joy: Free Pet Adoption For Seniors Near Me
Crackin' Up: A Deep Dive Into Crawfish Jokes
Article Recommendations
- Ultimate Guide To Elf Power Grip Primer Benefits Usage And Tips
- All About Bts Rm The Multitalented Leader Of The Global Sensation
- Latest Kannada Movies 2023 Download Movierulz