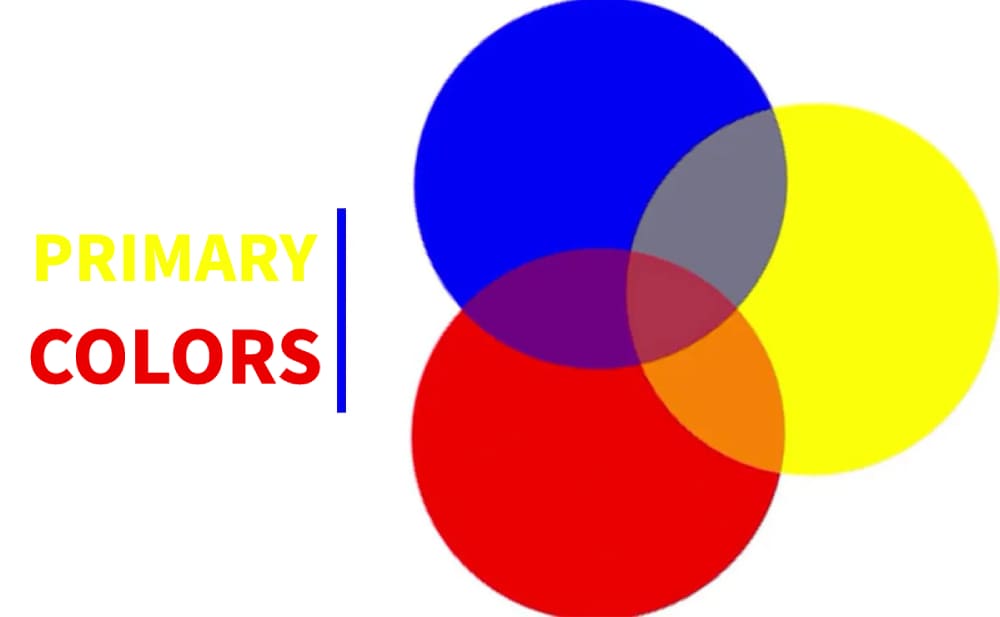
What are the primary colors? This question has intrigued artists, scientists, and educators alike for centuries. The primary colors form the foundation of our understanding of color theory and play a critical role in art, design, and even psychology. By delving into the primary colors, we unlock the secrets to creating every hue imaginable, influencing both our visual experiences and emotional responses.
Primary colors are more than just a basic concept taught in elementary school; they are a fundamental component of the color spectrum. Understanding these colors helps us grasp how different colors interact, how they are perceived, and how they can be combined to create an infinite array of new colors. Artists use this knowledge to mix colors effectively, while designers apply it to create visually appealing products and experiences.
In this comprehensive exploration of primary colors, we will uncover their definition and history, delve into the different color models, and examine their application across various fields. Whether you're an artist looking to refine your palette, a designer seeking to enhance your creations, or simply curious about the vivid world of color, this guide will provide the insight and knowledge you need. Let's embark on this colorful journey together.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Primary Colors
- The History and Evolution of Primary Colors
- Understanding Different Color Models
- Additive Color Model: RGB
- Subtractive Color Model: CMY and CMYK
- Primary Colors in the Artist’s Palette
- The Psychology of Primary Colors
- Cultural Significance of Primary Colors
- Application of Primary Colors in Design
- Role of Primary Colors in Education
- Primary Colors in Technology and Digital Media
- Influence of Primary Colors in Fashion
- Primary Colors in Nature
- The Future of Primary Colors
- FAQs About Primary Colors
- Conclusion
Definition of Primary Colors
Primary colors are defined as sets of colors that can be combined to create a broad spectrum of other colors. These colors are considered the "building blocks" of the color spectrum and cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Traditionally, the primary colors are red, blue, and yellow in the context of art and education, while in the digital realm, the primary colors are red, green, and blue.
The concept of primary colors is essential in understanding how colors blend and interact. In the traditional sense, mixing primary colors in various combinations results in secondary and tertiary colors, broadening the color palette available for use. This principle is fundamental to color theory and is widely used in art and design.
Primary colors also play a role in the science of light and human vision. They correspond to the peak sensitivities of the cone cells in our eyes, which are responsible for color vision. By understanding primary colors, we gain insight into how we perceive the world around us and how different colors can influence our emotions and behaviors.
The History and Evolution of Primary Colors
The concept of primary colors has evolved over time, influenced by scientific discoveries and cultural shifts. The idea dates back to ancient times, where early artists and philosophers sought to understand and categorize the colors in nature. The Greek philosopher Aristotle was one of the first to propose a theory of colors, suggesting that all colors derived from three primary colors.
During the Renaissance, artists like Leonardo da Vinci and scientists like Isaac Newton further explored the nature of colors. Newton's experiments with prisms demonstrated that white light contains a spectrum of colors, leading to the identification of red, blue, and yellow as primary colors in art. This triadic system became the foundation of color theory in art education.
In the 19th century, the development of color photography and printing processes introduced new color models, such as the RGB (red, green, blue) model used in digital media today. The understanding of primary colors continues to evolve, with ongoing research in color science and technology refining our knowledge and applications of these fundamental hues.
Understanding Different Color Models
Color models are systems used to describe and categorize colors based on their properties and interactions. They are essential in various fields, including art, design, printing, and digital media. Different color models use different sets of primary colors, each with its unique approach and application.
The two most widely recognized color models are the additive and subtractive models. The additive model, commonly used in digital screens and lighting, relies on red, green, and blue (RGB) as primary colors. By combining these colors in varying intensities, a vast array of colors can be produced.
The subtractive model, used in painting and printing, employs cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY) as primary colors. In this model, colors are created by subtracting varying degrees of light from white. The CMYK model, which adds black to the mix, is a common variant used in the printing industry.
Each color model has its strengths and limitations, and understanding their differences is crucial for effectively applying colors in various mediums and technologies.
Additive Color Model: RGB
The additive color model is based on the principle of combining different colors of light to create new colors. In this model, the primary colors are red, green, and blue (RGB). When these colors of light are combined in different intensities, they produce a wide range of colors, including white light.
This model is widely used in digital displays, such as computer monitors, televisions, and smartphones. In these devices, pixels are made up of tiny red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that can be adjusted to produce the desired colors. The RGB model is also used in lighting design, allowing for dynamic and customizable lighting effects.
Understanding the RGB model is essential for anyone working in digital media, as it forms the basis for color representation in most electronic devices. It is also a key component in color management systems, which ensure accurate color reproduction across different devices and platforms.
Subtractive Color Model: CMY and CMYK
The subtractive color model is used in traditional media, such as painting and printing, where colors are created by subtracting varying degrees of light from white. The primary colors in this model are cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY). When combined, these colors absorb certain wavelengths of light, leaving others to be reflected, resulting in the perception of different colors.
In printing, the CMYK model adds black (K) to enhance color depth and contrast. This model is widely used in the printing industry, as it allows for precise control over color reproduction and printing quality. Understanding the subtractive model is crucial for artists, designers, and print professionals, as it informs color mixing techniques and printing processes.
While the CMY and CMYK models are effective for traditional media, they have limitations in reproducing certain colors that are easily achieved in the additive model. As such, color management and calibration are essential in ensuring consistent and accurate color reproduction across different mediums.
Primary Colors in the Artist’s Palette
For artists, primary colors are the foundation of their creative work. By mastering the use of red, blue, and yellow, artists can mix and create a vast array of colors to bring their visions to life. The traditional color wheel, which is based on these primary colors, is a valuable tool for artists in understanding color relationships and harmony.
In painting, the ability to mix primary colors effectively is a fundamental skill. By combining these colors in different proportions, artists can create secondary colors (such as green, orange, and purple) and tertiary colors (such as vermilion and teal). This allows for a rich and diverse color palette, enabling artists to convey mood, emotion, and depth in their work.
Beyond painting, primary colors also play a role in other art forms, such as sculpture, textiles, and digital art. Understanding the properties and interactions of primary colors is essential for artists of all disciplines, as it informs their creative decisions and enhances their ability to communicate through color.
The Psychology of Primary Colors
Primary colors have a significant impact on our emotions and perceptions, influencing everything from our mood to our behavior. The study of color psychology explores how different colors affect our mental and emotional states and how they can be used to evoke specific responses.
Red, for example, is often associated with energy, passion, and excitement. It can stimulate the senses and increase heart rate, making it a popular choice for creating a sense of urgency or intensity. Blue, on the other hand, is associated with calmness, trust, and stability. It is often used in environments where relaxation and focus are desired.
Yellow is linked to feelings of happiness, warmth, and optimism. It can evoke a sense of positivity and creativity, making it a popular choice for inspiring and uplifting environments. Understanding the psychological impact of primary colors is valuable for designers, marketers, and educators, as it informs their use of color to influence and engage their audiences.
Cultural Significance of Primary Colors
Primary colors hold cultural significance across different societies and traditions, influencing art, fashion, and symbolism. The meanings and associations of colors can vary widely between cultures, adding depth and complexity to their use and interpretation.
In Western cultures, red is often associated with love, passion, and power, while in Eastern cultures, it is a symbol of luck and prosperity. Blue is commonly associated with calmness and trust in many cultures, but it can also represent mourning or sadness in others. Yellow is often linked to warmth and happiness, but it can also symbolize caution or deceit.
Understanding the cultural significance of primary colors is essential for global communication and design, as it ensures that colors are used appropriately and respectfully across different contexts. This awareness enhances the effectiveness and impact of color in conveying messages and emotions.
Application of Primary Colors in Design
In design, primary colors are used to create visually appealing and effective compositions. By understanding the principles of color theory and the interactions of primary colors, designers can craft harmonious and engaging designs that capture attention and convey meaning.
Primary colors are often used in branding and advertising to create memorable and recognizable visuals. The boldness and simplicity of primary colors make them effective for communicating messages quickly and clearly, enhancing brand identity and recognition.
In interior design, primary colors can be used to create dynamic and vibrant spaces. By combining and balancing these colors, designers can achieve a wide range of effects, from energizing and stimulating to calming and soothing. The strategic use of primary colors in design can enhance the functionality and appeal of spaces, making them more enjoyable and effective for their intended purposes.
Role of Primary Colors in Education
Primary colors play a vital role in education, particularly in early childhood development. Understanding and recognizing colors is a fundamental skill that supports cognitive and language development, as well as creativity and expression.
In art education, primary colors are used to teach students the basics of color theory and mixing. By experimenting with primary colors, students learn how to create new colors and understand color relationships, enhancing their artistic skills and appreciation.
Beyond art, primary colors are also used in educational materials and environments to support learning and engagement. The use of color can enhance visual learning, improve memory retention, and create stimulating and motivating learning spaces.
Primary Colors in Technology and Digital Media
In the realm of technology and digital media, primary colors are crucial for creating and displaying digital content. The RGB color model, based on red, green, and blue, is the standard for digital displays, allowing for the accurate representation of colors on screens.
Understanding the RGB model is essential for professionals working in digital media, as it informs color calibration, design, and production processes. The ability to accurately reproduce colors on digital devices is critical for ensuring consistency and quality across different platforms and mediums.
In addition to display technology, primary colors are also used in digital art and design, where they form the basis for creating visually striking and effective content. The knowledge of primary colors and their interactions is a key skill for digital artists and designers, enabling them to craft compelling and engaging experiences for their audiences.
Influence of Primary Colors in Fashion
In the world of fashion, primary colors are used to create bold and impactful designs. These colors are often associated with energy, confidence, and creativity, making them popular choices for fashion designers seeking to make a statement.
Primary colors are also used in fashion to convey specific messages and emotions. Red may be used to express passion and power, while blue can evoke a sense of calm and trust. Yellow is often associated with happiness and optimism, adding a sense of warmth and positivity to fashion designs.
The use of primary colors in fashion is not limited to clothing; it also extends to accessories, makeup, and branding. Understanding the cultural and psychological associations of primary colors is essential for fashion professionals, as it informs their design decisions and enhances their ability to connect with consumers.
Primary Colors in Nature
Primary colors are not just a human construct; they are also found in nature, influencing our perceptions and experiences of the natural world. From the vibrant red of a sunset to the deep blue of the ocean, primary colors play a significant role in our visual experiences and emotional responses.
In nature, primary colors can serve various functions, such as attracting pollinators, warning predators, or camouflaging animals. The use of color in nature is a fascinating area of study, highlighting the complex interactions between organisms and their environments.
Understanding the role of primary colors in nature enhances our appreciation of the natural world and informs our use of color in art, design, and communication. By observing and learning from nature, we can gain valuable insights into the power and potential of color.
The Future of Primary Colors
As our understanding of color continues to evolve, the future of primary colors holds exciting possibilities. Advances in technology and color science are expanding our knowledge and applications of color, opening new opportunities for creativity and innovation.
In the digital realm, developments in display technology and color management are enhancing our ability to reproduce and experience colors accurately and consistently. In art and design, new materials and techniques are pushing the boundaries of color creation and expression.
As we look to the future, the study and application of primary colors will continue to play a vital role in shaping our visual experiences and interactions. By embracing new knowledge and technologies, we can unlock the full potential of primary colors and their impact on our lives.
FAQs About Primary Colors
- What are the primary colors in art?
The primary colors in art are red, blue, and yellow. These colors cannot be created by mixing other colors and are used to create a wide range of other colors through mixing.
- What are the primary colors in digital media?
In digital media, the primary colors are red, green, and blue (RGB). These colors are used in the additive color model to create a wide range of colors on screens and displays.
- How do primary colors affect our emotions?
Primary colors can have a significant impact on our emotions. For example, red can evoke feelings of energy and passion, blue can create a sense of calm and trust, and yellow can inspire happiness and optimism.
- How are primary colors used in design?
Primary colors are used in design to create visually appealing and effective compositions. They are often used in branding, advertising, and interior design to convey messages and evoke specific emotions.
- What is the difference between additive and subtractive color models?
The additive color model (RGB) combines colors of light to create new colors, while the subtractive color model (CMY/CMYK) uses pigments to subtract light, creating colors by absorbing certain wavelengths.
- Why are primary colors important in education?
Primary colors are important in education because they support cognitive and language development, creativity, and expression. They are used to teach color theory and mixing, as well as to enhance learning materials and environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what are the primary colors is essential for anyone interested in art, design, and visual communication. These colors form the foundation of color theory and play a crucial role in creating and interpreting the world around us. By exploring the history, applications, and significance of primary colors, we gain valuable insights into their power and potential.
Whether you're an artist seeking to refine your palette, a designer looking to enhance your creations, or simply curious about the vibrant world of color, the knowledge of primary colors is a valuable tool. By embracing this understanding, we can unlock new possibilities for creativity, innovation, and connection through color.
For further exploration of primary colors and their applications, consider visiting resources such as [Color Matters](https://www.colormatters.com). This site offers extensive information on color theory, psychology, and applications, providing a wealth of knowledge for anyone interested in the fascinating world of color.
You Might Also Like
The Fascinating World Of Fish Pokémon: Unveiling The Mysteries Of Aquatic Pocket MonstersDiscovering The Best Tattoo Shops Near Me: A Guide To Quality And Creativity
The Gregarious Definition: Understanding Its Intricacies And Implications
Discover The Allure: The Ultimate Guide To Jimmy Choo Cologne
Zionist Meaning: Understanding The Evolution And Impact Of Zionism
Article Recommendations
- Chole Surreql A Delectable Dish Celebrating Flavor And Tradition
- The Dynamic Legacy Of David Lee Roth A Rock Icons Journey
- Unveiling The Personal Life Of Willem De Schryver A Glimpse Into His Partner And Relationship Journey